| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- page
- slab
- Kernel
- Network
- pmap
- slowpath
- vmalloc
- multiqueue
- BLOCK
- buddy_system
- NDK
- memory
- Android
- Apache
- fastpath
- kmalloc
- strex
- commit
- blk-mq
- allocator
- lruvec
- slub
- vm_area_struct
- mm_struct
- kafka
- 카프카
- spinlock
- Linux
- devicedriver
- proc
- Today
- Total
Art of Pr0gr4m
[Linux Kernel 5] mmap (메모리 매핑) 본문
리눅스 시스템 프로그래밍 경험이 있다면 메모리 매핑은 꽤 익숙할 것이다.
(만약 익숙치 않다면 꼭 다시 공부를 하기 바란다. 굉장히 중요하다.)
이번 포스트에선 커널이 메모리 매핑을 제공하기 위한 인터페이스를 살펴보고 예제를 작성해본다.
1. mmap interface
mmap 오퍼레이션을 저장하기 위한 구조체는 다음과 같다.
/*
* These are the virtual MM functions - opening of an area, closing and
* unmapping it (needed to keep files on disk up-to-date etc), pointer
* to the functions called when a no-page or a wp-page exception occurs.
*/
struct vm_operations_struct {
void (*open)(struct vm_area_struct * area);
void (*close)(struct vm_area_struct * area);
int (*split)(struct vm_area_struct * area, unsigned long addr);
int (*mremap)(struct vm_area_struct * area);
vm_fault_t (*fault)(struct vm_fault *vmf);
vm_fault_t (*huge_fault)(struct vm_fault *vmf,
enum page_entry_size pe_size);
void (*map_pages)(struct vm_fault *vmf,
pgoff_t start_pgoff, pgoff_t end_pgoff);
unsigned long (*pagesize)(struct vm_area_struct * area);
/* notification that a previously read-only page is about to become
* writable, if an error is returned it will cause a SIGBUS */
vm_fault_t (*page_mkwrite)(struct vm_fault *vmf);
/* same as page_mkwrite when using VM_PFNMAP|VM_MIXEDMAP */
vm_fault_t (*pfn_mkwrite)(struct vm_fault *vmf);
/* called by access_process_vm when get_user_pages() fails, typically
* for use by special VMAs that can switch between memory and hardware
*/
int (*access)(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long addr,
void *buf, int len, int write);
/* Called by the /proc/PID/maps code to ask the vma whether it
* has a special name. Returning non-NULL will also cause this
* vma to be dumped unconditionally. */
const char *(*name)(struct vm_area_struct *vma);
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
/*
* set_policy() op must add a reference to any non-NULL @new mempolicy
* to hold the policy upon return. Caller should pass NULL @new to
* remove a policy and fall back to surrounding context--i.e. do not
* install a MPOL_DEFAULT policy, nor the task or system default
* mempolicy.
*/
int (*set_policy)(struct vm_area_struct *vma, struct mempolicy *new);
/*
* get_policy() op must add reference [mpol_get()] to any policy at
* (vma,addr) marked as MPOL_SHARED. The shared policy infrastructure
* in mm/mempolicy.c will do this automatically.
* get_policy() must NOT add a ref if the policy at (vma,addr) is not
* marked as MPOL_SHARED. vma policies are protected by the mmap_sem.
* If no [shared/vma] mempolicy exists at the addr, get_policy() op
* must return NULL--i.e., do not "fallback" to task or system default
* policy.
*/
struct mempolicy *(*get_policy)(struct vm_area_struct *vma,
unsigned long addr);
#endif
/*
* Called by vm_normal_page() for special PTEs to find the
* page for @addr. This is useful if the default behavior
* (using pte_page()) would not find the correct page.
*/
struct page *(*find_special_page)(struct vm_area_struct *vma,
unsigned long addr);
};open은 매핑 초기화 오퍼레이션을, close는 매핑 해제 오퍼레이션을 정의한다.
fault 오퍼레이션은 Page fault가 일어났을 때 호출되는 오퍼레이션으로,
해당 핸들러에서 가상 메모리를 페이지로 매핑하는 핵심 작업을 수행하게 된다.
fault의 인자 struct vm_fault에는 다음과 같은 정보들이 포함되어 있다.
/*
* vm_fault is filled by the the pagefault handler and passed to the vma's
* ->fault function. The vma's ->fault is responsible for returning a bitmask
* of VM_FAULT_xxx flags that give details about how the fault was handled.
*
* MM layer fills up gfp_mask for page allocations but fault handler might
* alter it if its implementation requires a different allocation context.
*
* pgoff should be used in favour of virtual_address, if possible.
*/
struct vm_fault {
struct vm_area_struct *vma; /* Target VMA */
unsigned int flags; /* FAULT_FLAG_xxx flags */
gfp_t gfp_mask; /* gfp mask to be used for allocations */
pgoff_t pgoff; /* Logical page offset based on vma */
unsigned long address; /* Faulting virtual address */
pmd_t *pmd; /* Pointer to pmd entry matching
* the 'address' */
pud_t *pud; /* Pointer to pud entry matching
* the 'address'
*/
pte_t orig_pte; /* Value of PTE at the time of fault */
struct page *cow_page; /* Page handler may use for COW fault */
struct mem_cgroup *memcg; /* Cgroup cow_page belongs to */
struct page *page; /* ->fault handlers should return a
* page here, unless VM_FAULT_NOPAGE
* is set (which is also implied by
* VM_FAULT_ERROR).
*/
/* These three entries are valid only while holding ptl lock */
pte_t *pte; /* Pointer to pte entry matching
* the 'address'. NULL if the page
* table hasn't been allocated.
*/
spinlock_t *ptl; /* Page table lock.
* Protects pte page table if 'pte'
* is not NULL, otherwise pmd.
*/
pgtable_t prealloc_pte; /* Pre-allocated pte page table.
* vm_ops->map_pages() calls
* alloc_set_pte() from atomic context.
* do_fault_around() pre-allocates
* page table to avoid allocation from
* atomic context.
*/
};상대적으로 최신 구조체라 그런지 주석에 상세하게 멤버들의 설명이 적혀있기에 참고한다.
2. 메모리 매핑 처리 과정
시스템콜 mmap을 호출하면 여타 시스템 콜과 같이 sys_mmap을 호출한다. (현재 시스템콜 번호 9번이다.)
sys_mmap은 old_mmap으로 정의되어 있으며,
시스템콜 old_mmap의 정의에서는 ksys_mmap_pgoff를 호출한다.
ksys_mmap_pgoff는 flag에 따른 처리(huge file setup 등)을 수행하고 vm_mmap_pgoff를 호출한다.
다시 vm_mmap_pgoff는 do_mmap_pgoff -> do_mmap를 호출한다.
do_mmap에서는 매핑을 위한 각종 사전 작업(주소 처리, 권한 처리, 기타 플래그 처리 등)을 처리 한 후,
실제 매핑을 위한 get_unmapped_area와 매핑 외 처리(공유, merge 등)를 위한 mmap_region을 호출한다.
핵심인 get_unmapped_area의 정의는 다음과 같다.
unsigned long
get_unmapped_area(struct file *file, unsigned long addr, unsigned long len,
unsigned long pgoff, unsigned long flags)
{
unsigned long (*get_area)(struct file *, unsigned long,
unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
unsigned long error = arch_mmap_check(addr, len, flags);
if (error)
return error;
/* Careful about overflows.. */
if (len > TASK_SIZE)
return -ENOMEM;
get_area = current->mm->get_unmapped_area;
if (file) {
if (file->f_op->get_unmapped_area)
get_area = file->f_op->get_unmapped_area;
} else if (flags & MAP_SHARED) {
/*
* mmap_region() will call shmem_zero_setup() to create a file,
* so use shmem's get_unmapped_area in case it can be huge.
* do_mmap_pgoff() will clear pgoff, so match alignment.
*/
pgoff = 0;
get_area = shmem_get_unmapped_area;
}
addr = get_area(file, addr, len, pgoff, flags);
if (IS_ERR_VALUE(addr))
return addr;
if (addr > TASK_SIZE - len)
return -ENOMEM;
if (offset_in_page(addr))
return -EINVAL;
error = security_mmap_addr(addr);
return error ? error : addr;
}
파일 매핑이라면 get_area 함수 포인터에 파일 매핑이라면 file->f_op->get_unmapped_area를, 공유 매핑이라면 shmem_get_unmapped_area를, 그 외엔 current->mm->get_unmapped_area를 저장하여 호출한다.
파일 매핑의 경우 파일 시스템에서 정의한 get_unmapped_area가 있다면 그것을 호출하고, 없다면 generic_file_mmap을 호출하여 매핑한다.
generic_file_mmap에선 generic_file_vm_ops를 등록하는데, 해당 정의는 다음과 같다.
const struct vm_operations_struct generic_file_vm_ops = {
.fault = filemap_fault,
.map_pages = filemap_map_pages,
.page_mkwrite = filemap_page_mkwrite,
};즉, 여기에 등록되어 있는 filemap_fault 함수를 참고하면 제너릭한 파일 매핑 오퍼레이션을 만들 수 있다.
공유 메모리가 아닌 메모리 매핑의 경우엔 힙 공간 매핑엔 arch_get_unmapped_area를, 스탭 공간 매핑엔 arch_get_unmapped_area_topdown을 호출하게 된다.
그리고 보통 내부적으로 다시 unmapped_area(_topdown)을 호출하여 매핑을 수행한다.
3. mmap 드라이버 예제 소스
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/ptrace.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <uapi/linux/fs.h>
#define DEV_NAME "mmap"
#define DATA_SIZE (1 * (1 << PAGE_SHIFT)) // one page
static const unsigned int MINOR_BASE = 0;
static const unsigned int MINOR_NUM = 1;
static unsigned int mmapdev_major;
static struct cdev *mmapdev_cdev = NULL;
static struct class *mmapdev_class = NULL;
static int *data = NULL;
static atomic_t counter = ATOMIC_INIT(0);
static void mmap_vma_open(struct vm_area_struct *vma)
{
atomic_inc(&counter);
printk("%s: %d\n", __func__, atomic_read(&counter));
printk("vm_pgoff: %08lx\n", vma->vm_pgoff);
printk("vm_start: %08lx\n", vma->vm_start);
printk("vm_end : %08lx\n", vma->vm_end);
}
static void mmap_vma_close(struct vm_area_struct *vma)
{
atomic_dec(&counter);
printk("%s: %d\n", __func__, atomic_read(&counter));
}
static vm_fault_t mmap_vm_fault(struct vm_fault *vmf)
{
struct page *page = NULL;
unsigned long offset = 0;
void *page_ptr = NULL;
printk("%s\n", __func__);
if (vmf == NULL)
return VM_FAULT_SIGBUS;
offset = vmf->address - vmf->vma->vm_start;
if (offset >= DATA_SIZE)
return VM_FAULT_SIGBUS;
page_ptr = data + offset;
page = vmalloc_to_page(page_ptr);
get_page(page);
vmf->page = page;
return 0;
}
static struct vm_operations_struct vma_ops = {
.open = mmap_vma_open,
.close = mmap_vma_close,
.fault = mmap_vm_fault
};
static int mmap_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
static int mmap_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
static int mmap_remap(struct file *filp, struct vm_area_struct *vma)
{
printk("%s\n", __func__);
vma->vm_flags |= VM_IO;
vma->vm_ops = &vma_ops;
mmap_vma_open(vma);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t mmap_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf,
size_t count, loff_t *offset)
{
if (*offset > DATA_SIZE)
return -EIO;
copy_to_user(buf, (void *)(data + *offset), count);
*offset += 1;
filp->f_pos = *offset;
return count;
}
static ssize_t mmap_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t count, loff_t *offset)
{
copy_from_user((void *)(data + *offset), buf, count);
*offset += 1;
filp->f_pos = *offset;
return count;
}
static loff_t mmap_lseek(struct file *filp, loff_t offset, int org)
{
loff_t ret;
//printk("%s\n", __func__);
switch (org)
{
case SEEK_SET:
filp->f_pos = offset;
ret = filp->f_pos;
force_successful_syscall_return();
break;
case SEEK_CUR:
filp->f_pos += offset;
ret = filp->f_pos;
force_successful_syscall_return();
break;
default:
ret = -EINVAL;
}
return ret;
}
struct file_operations mmap_fops = {
.open = mmap_open,
.release = mmap_release,
.read = mmap_read,
.write = mmap_write,
.mmap = mmap_remap,
.llseek = mmap_lseek
};
static int __init _mmap_init(void)
{
int alloc_ret = 0, cdev_err = 0;
dev_t dev;
mmapdev_cdev = cdev_alloc();
alloc_ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, MINOR_BASE, MINOR_NUM, DEV_NAME);
if (alloc_ret != 0) {
printk(KERN_ERR "alloc_chrdev_region = %d\n", alloc_ret);
return -1;
}
mmapdev_major = MAJOR(dev);
dev = MKDEV(mmapdev_major, MINOR_BASE);
cdev_init(mmapdev_cdev, &mmap_fops);
mmapdev_cdev->owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_err = cdev_add(mmapdev_cdev, dev, MINOR_NUM);
if (cdev_err != 0) {
printk(KERN_ERR "cdev_add = %d\n", cdev_err);
goto OUT2;
}
mmapdev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "mmap_device");
if (IS_ERR(mmapdev_class)) {
printk(KERN_ERR "class_create\n");
goto OUT;
}
device_create(mmapdev_class, NULL, MKDEV(mmapdev_major, MINOR_BASE), NULL, DEV_NAME);
data = vmalloc(DATA_SIZE);
if (data == NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR "vmalloc failed\n");
goto OUT;
}
memset(data, 0, DATA_SIZE);
return 0;
OUT:
cdev_del(mmapdev_cdev);
OUT2:
unregister_chrdev_region(dev, MINOR_NUM);
return -1;
}
static void __exit _mmap_exit(void)
{
dev_t dev = MKDEV(mmapdev_major, MINOR_BASE);
device_destroy(mmapdev_class, dev);
class_destroy(mmapdev_class);
cdev_del(mmapdev_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(dev, MINOR_NUM);
vfree(data);
}
module_init(_mmap_init);
module_exit(_mmap_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");매핑 초기화 시 호출될 mmap_vma_open 함수에서는 카운터를 증가시킨 후 vma 정보를 출력하고 있다.
매핑 해제 시 호출될 mmap_vma_close 함수에서는 카운터를 감소시킨다.
page fault 시 호출될 mmap_vm_fault에서는 핵심적인 매핑 역할을 수행하고 있다.
init 함수에서 메모리 매핑에 사용하기 위하여 vmalloc으로 할당한 커널 데이터의 매핑할 페이지를 구해서 페이지 카운터를 증가시키고 vmf의 페이지로 등록한다.
디바이스에 등록할 구조체 mmap_fops의 mmap 오퍼레이션으로 등록할 mmap_remap 함수에선 vma_ops를 등록하고 mmap_vma_open을 호출한다.
4. 테스트 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#if 1
#define DEV_NAME "/dev/mmap"
#else
#define DEV_NAME "test.dat"
#endif
void create_data(void)
{
int fd, i;
printf("%s\n", __func__);
fd = open(DEV_NAME, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
write(fd, &i, sizeof(int));
close(fd);
}
void display_data(void)
{
int fd = 0, data = 0, i;
printf("%s\n", __func__);
fd = open(DEV_NAME, O_RDONLY);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
if (read(fd, &data, sizeof(int)) == 4)
printf("%4d", data);
puts("");
close(fd);
}
void change_data(void)
{
int fd, data;
fd = open(DEV_NAME, O_RDWR);
read(fd, &data, sizeof(int));
data += 100;
write(fd, &data, sizeof(int));
close(fd);
}
void mmap_data(void)
{
int *mapped = NULL;
int fd;
fd = open(DEV_NAME, O_RDWR);
mapped = mmap(0, 4096, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (mapped == NULL)
return;
mapped[7] += 200;
msync(mapped, 4096, MS_ASYNC);
munmap(mapped, 4096);
close(fd);
}
int main(void)
{
create_data();
display_data();
change_data();
display_data();
mmap_data();
display_data();
return 0;
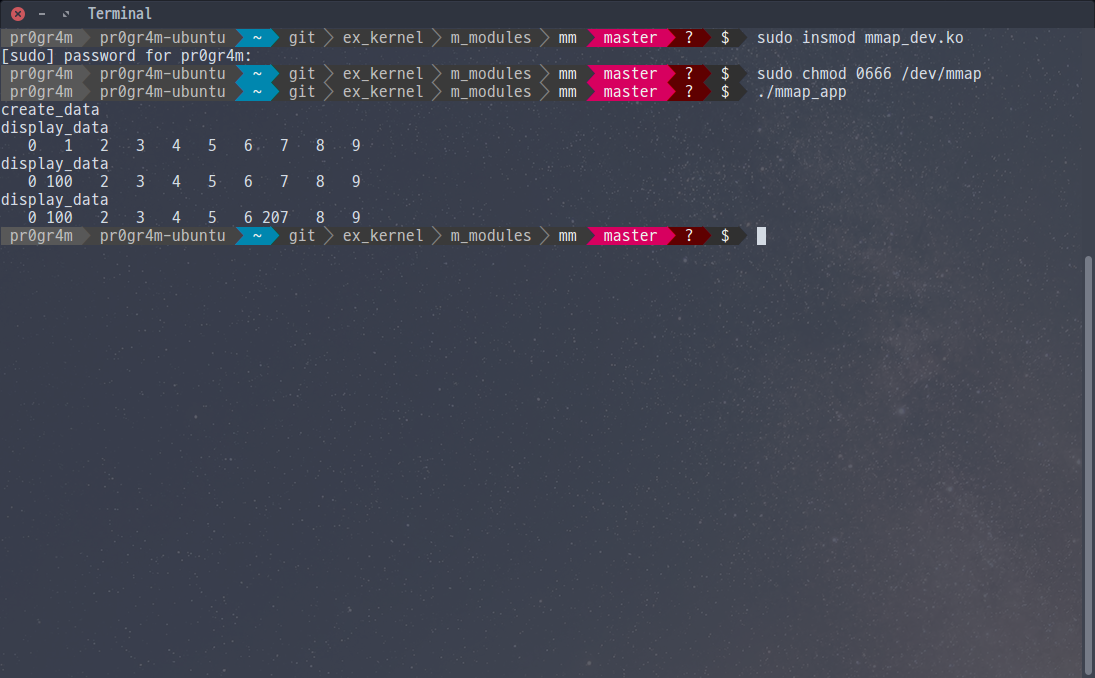
}생성된 디바이스의 읽기 / 쓰기 / 매핑을 테스트한다.
매크로를 0으로 바꾸면 일반 파일시스템 파일에 대해 같은 작업을 수행한다.
5. 실행 결과

'IT > Linux Kernel' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Linux Kernel 5] Process Memory Viewer HOL (0) | 2020.05.17 |
|---|---|
| [Linux Kernel 5] LRU (Memory Reclaim) (3) | 2020.05.17 |
| [Linux Kernel 5] Slab & Slub Allocator #2 (0) | 2020.05.17 |
| [Linux Kernel 5] Slab & Slub Allocator #1 (0) | 2020.05.15 |
| [Linux Kernel 5] Buddy System (fastpath & slowpath) (1) | 2020.05.14 |




